
Architect: nArchitects
Location: Lacoste, France
Project Completion Year: July 2006
Design Team: Eric Bunge, Mimi Hoang (Partners); Daniela Zimmer (Project Architect), Kazuya Katagiri, Takuya Shinoda, Shuji Suzumori / Fabrication by nARCHITECTS and SCAD (Jim Bischoff, Michael Gunter, Cindy Hartness, Michael Porten, Ryan Townsend, Troy Wandzel, with Natalie Bray and Sarah Walko)
Client: Savannah College of Art and Design (SCAD)
Program: Ephemeral pavilions
Photographs: Daniela Zimmer & nArchitects
Windshape was an ephemeral structure commissioned by the Savannah College of Art & Design (SCAD) as a venue and gathering space near their Provence campus in Lacoste, France. Built by nARCHITECTS and a team of SCAD students over a period of five weeks, Windshape became the small town’s main public meeting space, and hosted concerts, exhibitions, and ceremonies throughout the summer of 2006.
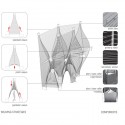
Windshape was conceived as two eight-meter-high pavilions that dynamically changed with the Provençale wind. A vine-like structural network of white plastic pipes, joined together and stretched apart by aluminum collars, emerged from the limestone walls and terraces of Lacoste’s hillside. Fifty kilometers of white polypropylene string was threaded through the lattice to create swaying enclosures. The string was woven into dense regions and surfaces and pinched to define doorways, windows, and spaces for seating.
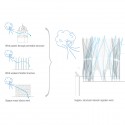
By varying the degree of tension in the string, nARCHITECTS built Windshape to respond to the wind in several ways, from rhythmic oscillations to fast ripples across its surfaces. During heavy winds, Windshape moved dramatically, and made a hissing sound akin to dozens of jumpropes. The pavilions took on a multitude of temporary forms over the course of the summer, as they billowed in and out, and momentarily came to rest. In this way, the local winds and the Mistral gave shape to constantly mutating structures. The pavilions were illuminated at night against the backdrop of the Marquis de Sade’s castle, and were visible from as far away as the village of Bonnieux, 5 kilometers away.
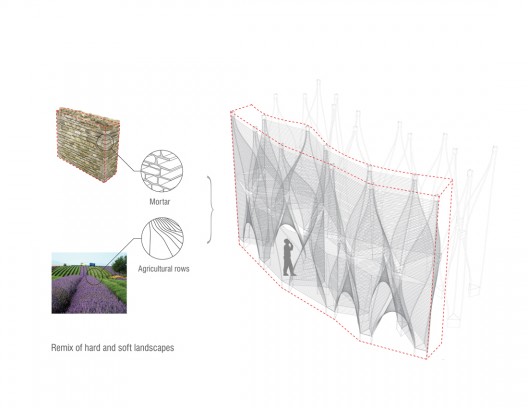
The pavilions’ design reflects a desire to remix the hard and soft landscapes of Provence in an innovative tectonic system. The village of Lacoste appears hewn out of limestone, its streets and network of terraces seemingly chiseled out as voids in the hillside. In contrast, the surrounding fields, vineyards, and lavender bushes form a luminous, soft, and changeable landscape. Windshape refers in its exterior form and angular geometry to the medieval townscape, while echoing the mutating, softer agricultural landscape in its internal experience and dynamic qualities.
Windshape was a laboratory that allowed us to test the idea of a building that can respond to natural stimuli. Rather than simply sheltering us from the elements, buildings of the future could connect inhabitants to their environment, reminding them of its strength and beauty.
Construction Process
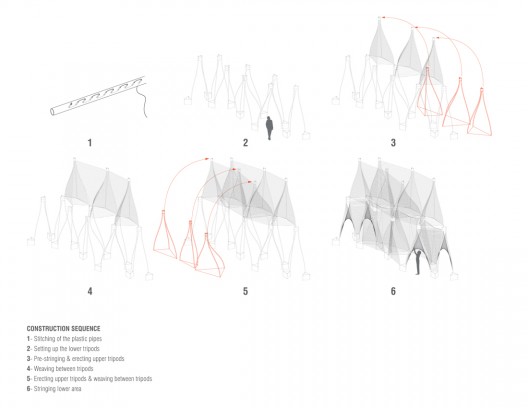
Windshape was constructed by nARCHITECTS and a team of SCAD students over a period of five weeks. The architects developed a construction sequence that optimized the use of measured and non-measured fabrication methods. The basic components of string, plastic pipes and aluminum collars were all digitally modeled and translated into a set of 2D drawings and data. To achieve the project’s complex, interwoven geometries, the pavilions were built as a series of stacked and staggered “tripods”. Comprised of groups of three pipes inserted into an aluminum collar, the tripods were pre-assembled, woven with string on the ground, and hoisted in place. Interstitial string surfaces were then woven in between the tripods in the air.
nARCHITECTS exploited the different properties of two weak and supple materials to create a strong yet elastic structural network. Similar to an archer’s bow, the pipes were placed in bending and the string in tension to achieve structural integrity as well as a desired range of movement in the wind. The interdependent structural system of string, pipes and collars required a flexible fabrication method. An initial stitching of string through the pipes allowed for improvisation in weaving strategies to provide enclosure, openings or stability. In this way, Windshape’s indeterminate structure relied equally on precise translations from digital models as well as in-situ building tactics.
- Construction Process
- Construction Process
- Construction Process
- Construction Process
- Construction Process
- Construction Process
- Construction Process
- Construction Process
- Construction Process
- Construction Process
- general plan
- construction sequence diagram
- landscapes diagram
- weaving diagram
- wind effect diagram









































Keine Kommentare:
Kommentar veröffentlichen